Biological
Applications
Gene Therapy
Applications Analysis of Gene Therapy Vectors and Nanomedicines
Spectradyne’s microfluidic technology has powerful applications in nanomedicine
Overview
Accurate quantification of gene therapy vectors and nanomedicines is critical at all stages of research and product development, whether for characterizing a production step or obtaining an accurate titer before assessing bioactivity. Spectradyne’s nCS2TM and ARCTM quantify all types of nanoparticle-based therapeutics quickly and accurately, and require only 3 microliters of the sample per measurement. The ARC instrument adds a fluorescent pheontyping capability to the particle size and concentration provided by Spectradyne’s nCS2.
Quantifying a virus-based drug product
The figure below shows nCS2TM measurements of a proprietary virus-based drug product as it progresses through three stages of purification. While each stage of purification increases the concentration of particles over a broad size range, a clear enrichment of virus product is obtained with the second stage. These measurements provided the manufacturer of this product with a highly detailed picture of the purification process, and insights for optimization that could not have been obtained with any other method.
Gene therapy vectors
Because the nCS2 uses an electrical method, not light scattering, to count and size nanoparticles, it measures all particle types equally well. As a result, researchers count on the nCS2 every day to measure diverse range of gene therapy vectors and other nanomedicines, including:
- Lentivirus, retrovirus, HSV and others
- Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)
- Liposomes
- Polymeric nanoparticles
- Milled drug particles (API crystals)
Fluorescent phenotyping
Spectradyne’s ARC combines the microfluidic resistive pulse sensing of the nCS1 with a particle-by-particle fluorescence detection, allowing phenotyping combined with particle size and concentration measurements. The applications of this fluorescence-extended MRPS instrument allows the ARC to measure a diverse range of nanomedicine targets, including:
- Polymeric nanoparticles
- Milled drug particles (API crystals)
- Lentivirus, retrovirus, HSV and others
- Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)
- Liposomes
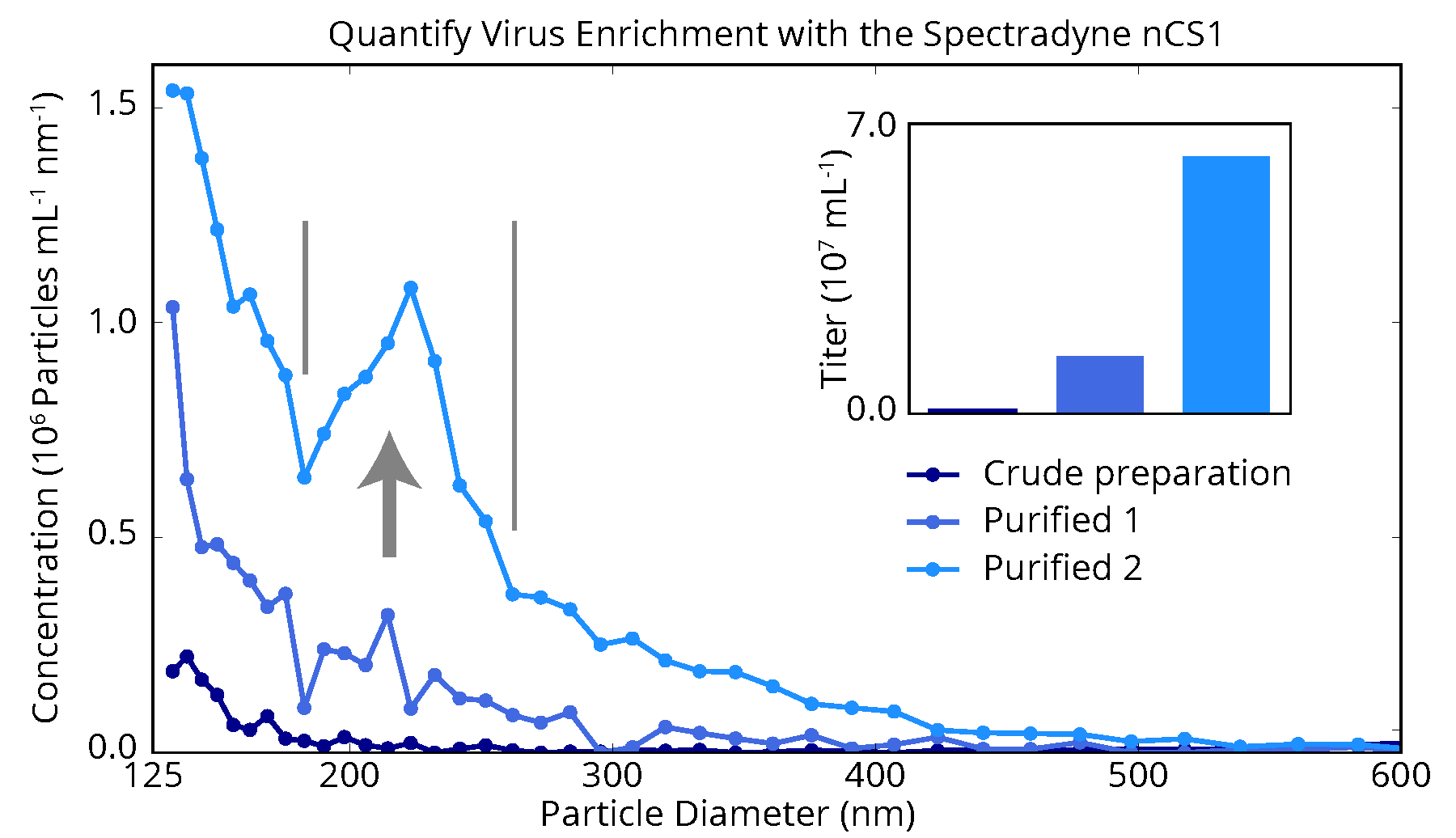
Spectradyne’s nCS2 enables monitoring virus purification stages
A virus-based drug product measured by the nCS2 after various stages of purification. Enrichment of the virus is clearly observed after the second purification step, and could not be measured so directly and practically using any other technology. Such high-resolution and quantitative measurements as these cannot be obtained with other technology, and enable more effective analysis of process parameters at all stages of the drug development process.